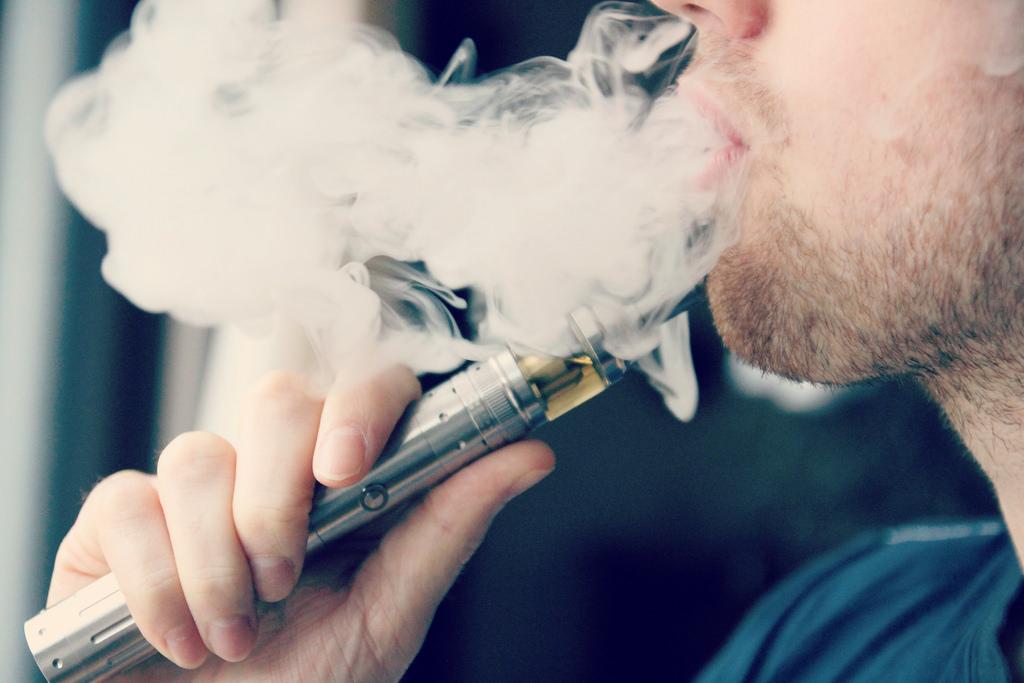
Though smoking traditional tobacco cigarettes has declined over the years, electronic nicotine delivery systems, known more commonly as electronic cigarettes, have risen in popularity among teenagers, with about 3 million reportedly smoking them in 2015, according to a report by the Center for Disease Control.
Coinciding with the rise in e-cigarette use, there have been increased concerns regarding the potential side effects and overall health impact of these devices.
Electronic cigarettes or “vapes” are devices which are driven by battery power allowing users to inhale the vapor which may often contain nicotine and other flavorings. According to the National Institute of Drug Abuse website, e-cigarettes have the same structure: a mouthpiece for inhalation of the vapors, a source of power (the battery), a cartridge which stores the solution and an atomizer. The user has to puff into the e-cig to activate the heating mechanism to vaporize the liquid and then would inhale the vapor, the website stated.
The side effects of vaping have been difficult to definitively pinpoint given the variability of vaping devices, e-cigarette fluids, and delivery methods. However, most e-cigarette fluids include nicotine, whose health consequences have been well documented, including inflammation in lung tissue and reduced ability of lung tissue to act as a barrier against foreign substances. Researchers at Indiana University also found that e-cigarette fluids without nicotine disrupt the ability of lung cells to serve as barriers to foreign agents.
Furthermore, e-cigarettes pose a unique side effect apart from traditional cigarettes. This is because although e-cigarette fluid components are approved by the FDA as “Generally Recognized As Safe,” their toxicity changes when heated. When e-cigarette fluid is heated, it produces compounds known as carbonyls, which include formaldehyde and acrolein. Acrolein is especially concerning because it has been linked to increased risk of cardiovascular disease among users.
Based on a study done by the UK Department of Health, e-cigarettes are considered safer than the traditional tobacco cigarette because they do not involve combustion reaction. The study also mentioned that e-cigarettes have the potential to be an alternative to smoking tobacco cigarettes. However, the American Heart Association also confirmed the sentiment because e-cigarettes do not contain as much less harmful ingredients than usual tobacco based items. The lack of combustion in e-cigarettes makes them safer because there is less risk of second hand smoking and because inhaling vapor is less consequential than inhaling smoke. This point of view is also shared by vaping360.com, which is the world’s largest pro-vaping website.
General consensus among public health officials is that the use of vaping devices would not be nearly as alarming if it were merely used as a substitute for traditional cigarettes. However, many e-cigarette users, especially adolescents, start with the product as a gateway to other potentially hazardous behaviors.
Data from a study conducted by the National Institute on Drug Abuse provides evidence for this claim, reporting that nearly 31% of vaping device users started smoking traditional cigarettes within six months. As the FDA has strengthened regulations on e-cigarette manufacturers and more data is collected regarding the health consequences of vaping, researchers caution that while current data suggests e-cigarettes are less dangerous than traditional cigarettes, they are not objectively safe.
Written by Marzia Rahman and Siri Uppuluri
Photo Credit to Vaping 360